Early drug forming screening
The early drug formation of compounds can be studied through toxicity prediction, pharmacokinetic screening, and efficacy screening studies, including cardiac toxicity risk prediction, tolerance dose of related species, bioavailability, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity.
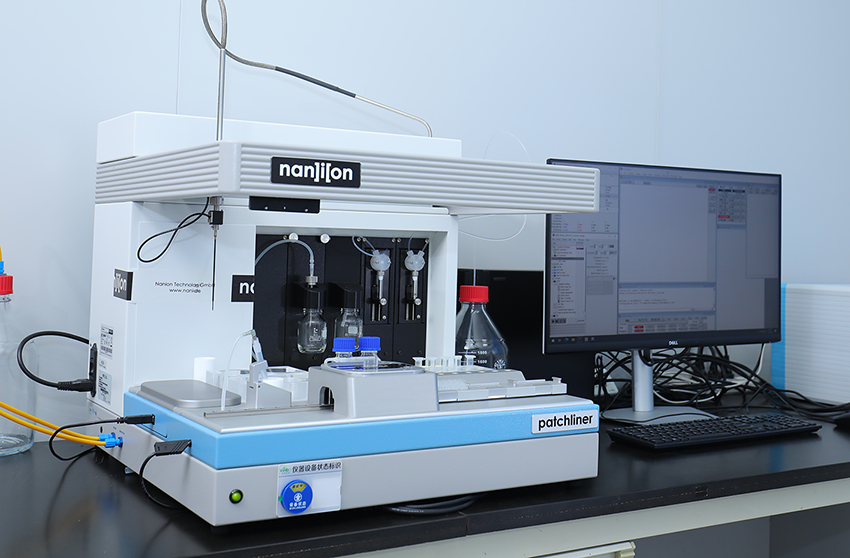
■ Non GLP cardiovascular safety screening test: hERG patch clamp
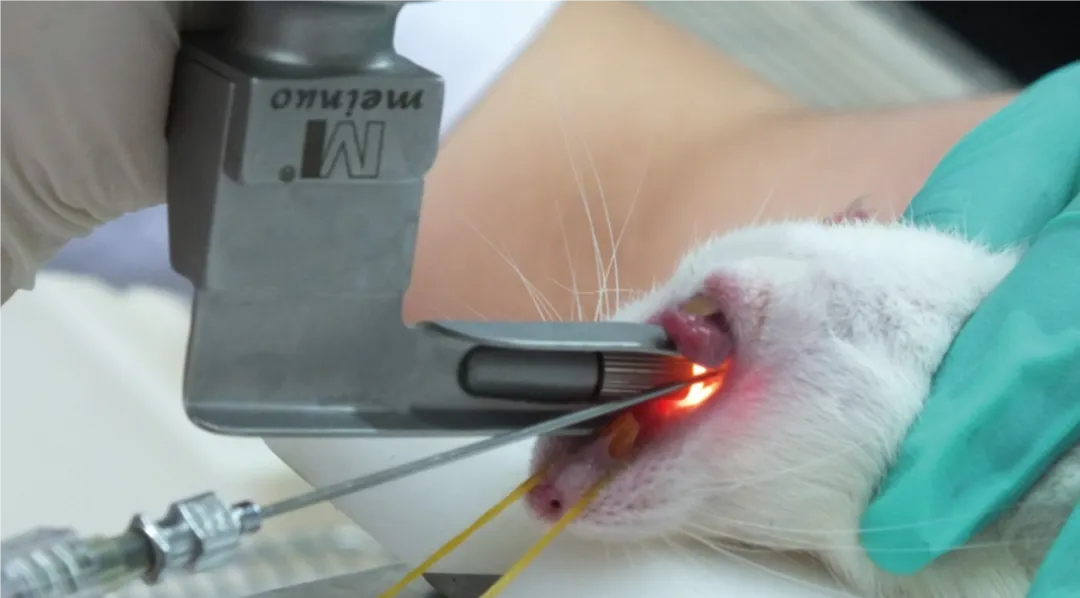
■ Tolerance exploration: rats, mice, dogs, monkeys
■ Cytotoxicity screening study
■ Genotoxicity screening study
■ Non GLP cardiovascular safety screening test: hERG patch clamp
■ Tolerance exploration: rats, mice, dogs, monkeys
■ Cytotoxicity screening study
■ Genotoxicity screening study
Toxicity prediction and screening
 Service items
Service items
■ Non GLP cardiovascular safety screening test: hERG patch clamp
■ Tolerance exploration: rats, mice, dogs, monkeys
■ Cytotoxicity screening study
■ Genotoxicity screening study
■ Tolerance exploration: rats, mice, dogs, monkeys
■ Cytotoxicity screening study
■ Genotoxicity screening study
Pharmacokinetic screening
 Service items
Service items
■ Bioavailability
■ Internal exposure
■ Enzyme inhibition
■ Enzyme induction
■ Related species screening research
■ Internal exposure
■ Enzyme inhibition
■ Enzyme induction
■ Related species screening research
Pharmacodynamic screening
 Service items
Service items
Pharmacodynamic studies can be used to predict the effectiveness of drugs in animals. The established models include:
■ Neuropsychiatric diseases: cerebral ischemia model, cerebral ischemia reperfusion model
■ Immune related diseases: arthritis model
■ Tumor: subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor
■ Respiratory diseases: pulmonary fibrosis model, pulmonary embolism
■ Digestive system diseases: various gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, reflux esophagitis, functional constipation model, diarrhea model
■Circulation and blood system diseases: acute and chronic heart failure, myocardial ischemia, myocardial ischemia reperfusion, myocardial infarction
■ Metabolic system diseases: diabetes model, obesity model, hypopituitarism model, clamp test■ Neuropsychiatric diseases: cerebral ischemia model, cerebral ischemia reperfusion model
■ Immune related diseases: arthritis model
■ Tumor: subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor
 Service advantages
Service advantages
>Jugular sinus blood sampling technique:
The animals do not need anesthesia, with small trauma, in line with animal ethics, and can meet the requirements of PK/TK blood collection.
>Bile duct intubation technique in conscious rats:
Bile collection in conscious rats lasting more than 72 hours can be achieved by means of bile duct intubation and external catheterization.
>Cerebrospinal fluid collection technology:
Cerebrospinal fluid of conscious/anesthetized animals can be collected for the study of blood-brain barrier permeability.
The animals do not need anesthesia, with small trauma, in line with animal ethics, and can meet the requirements of PK/TK blood collection.
>Bile duct intubation technique in conscious rats:
Bile collection in conscious rats lasting more than 72 hours can be achieved by means of bile duct intubation and external catheterization.
>Cerebrospinal fluid collection technology:
Cerebrospinal fluid of conscious/anesthetized animals can be collected for the study of blood-brain barrier permeability.